Ng tube anti reflux valve – Delving into the realm of NG tube anti-reflux valves, this comprehensive guide unveils the intricacies of this medical device, exploring its purpose, mechanism of action, and clinical applications. Join us as we navigate the world of NG tube anti-reflux valves, unraveling their significance in managing reflux and ensuring patient comfort.
An NG tube anti-reflux valve is a specialized medical device designed to prevent gastric contents from refluxing back into the esophagus. It plays a crucial role in managing conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and other reflux-related disorders, providing relief from discomfort and potential complications.
Introduction
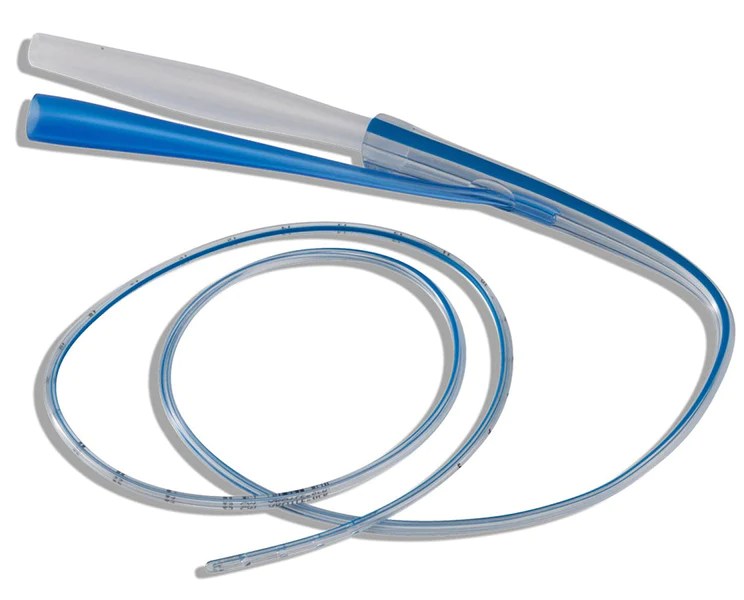
An NG tube anti-reflux valve is a device that is inserted into the nose and passed down into the stomach through the esophagus. It is used to prevent stomach contents from flowing back up into the esophagus, which can cause heartburn, regurgitation, and other problems.
The valve works by creating a one-way seal between the stomach and the esophagus. When the stomach contracts to push food down into the intestines, the valve opens to allow the food to pass through. When the stomach relaxes, the valve closes to prevent stomach contents from flowing back up into the esophagus.
Mechanism of Action
The NG tube anti-reflux valve is made of a soft, flexible material that is gentle on the esophagus. It is typically inserted by a doctor or nurse, and it can be left in place for several weeks or months.
Ng tube anti reflux valves are medical devices used to prevent stomach contents from flowing back into the esophagus. These valves can be helpful for people who have difficulty swallowing or who experience frequent heartburn or regurgitation. Maestro puedo ir al bano is a Spanish phrase that means “Teacher, can I go to the bathroom?” This phrase is often used by children in school who need to use the restroom.
Ng tube anti reflux valves and maestro puedo ir al bano are both related to the topic of bodily functions and the need to control them.
The valve is effective in preventing reflux in most cases. However, it is important to note that it is not a cure for reflux. It can only help to prevent stomach contents from flowing back up into the esophagus. If you have reflux, you will still need to take other measures to manage your condition, such as eating a healthy diet, avoiding certain foods and drinks, and taking medication.
Indications for Use
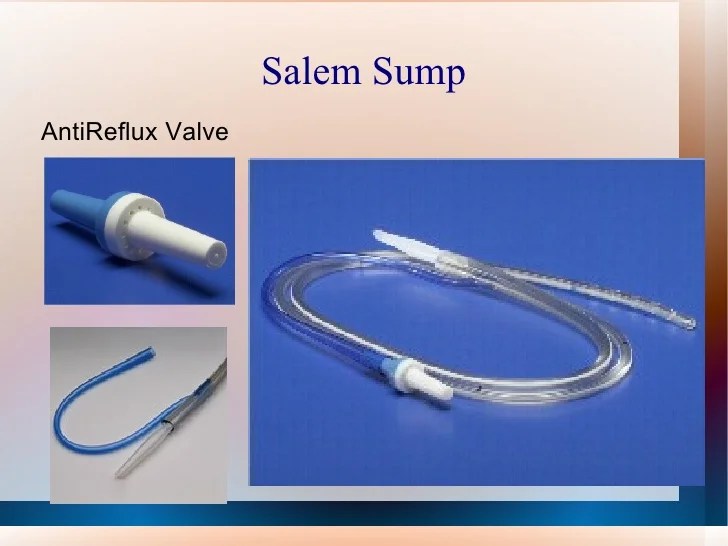
An NG tube anti-reflux valve is a device that is inserted into the nose and throat to help prevent reflux, or the backward flow of stomach contents into the esophagus. It is typically used in patients who are at high risk for reflux, such as those who have had recent surgery or who are on mechanical ventilation.
The most common clinical indications for using an NG tube anti-reflux valve include:
- Preventing aspiration pneumonia in patients who are at high risk for reflux, such as those who have had recent surgery or who are on mechanical ventilation.
- Reducing the risk of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) in patients who have frequent heartburn or regurgitation.
- Treating gastroparesis, a condition in which the stomach takes too long to empty.
- Providing enteral nutrition to patients who are unable to eat or drink by mouth.
Contraindications
There are a few contraindications to the use of an NG tube anti-reflux valve, including:
- Esophageal stricture, a narrowing of the esophagus that could make it difficult to insert the tube.
- Tracheoesophageal fistula, an abnormal connection between the trachea and the esophagus.
- Active bleeding from the esophagus or stomach.
Types of NG Tube Anti-Reflux Valves
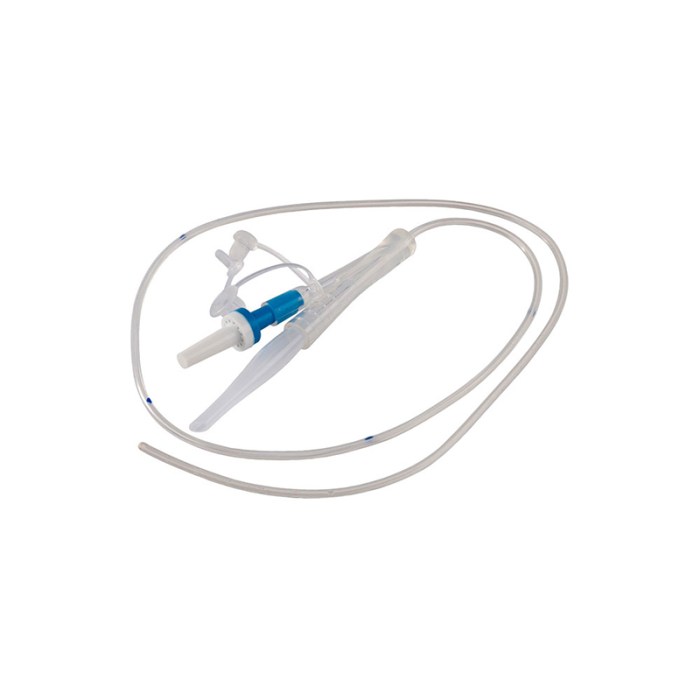

NG tube anti-reflux valves come in various types, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences can help healthcare professionals choose the most suitable valve for each patient.
Cuffed vs. Non-Cuffed Valves
Cuffed valves have an inflatable cuff that creates a seal around the NG tube, preventing reflux. Non-cuffed valves do not have a cuff and rely on the natural anatomy of the esophagus to prevent reflux.
- Advantages of Cuffed Valves:
- More effective in preventing reflux
- Can be used in patients with weak esophageal sphincters
- Disadvantages of Cuffed Valves:
- Can cause discomfort or pain
- May increase the risk of aspiration
- Advantages of Non-Cuffed Valves:
- More comfortable for patients
- Lower risk of aspiration
- Disadvantages of Non-Cuffed Valves:
- Less effective in preventing reflux
- May not be suitable for patients with weak esophageal sphincters
Insertion and Removal
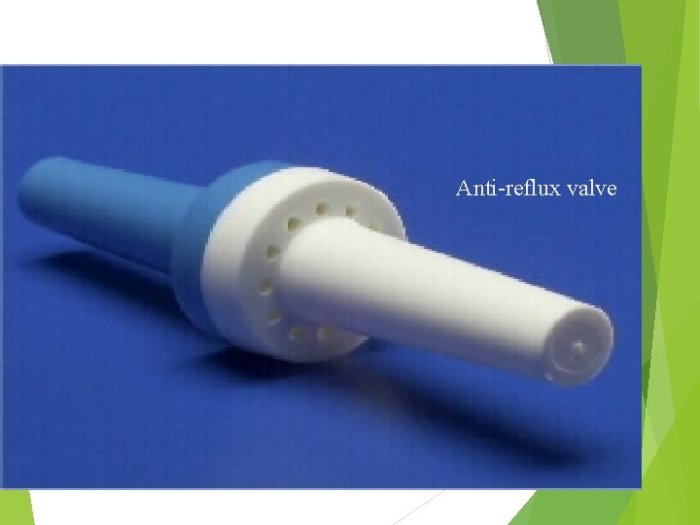

Inserting and removing an NG tube anti-reflux valve is a procedure that requires careful technique and attention to detail. It is typically performed by a healthcare professional, such as a nurse or doctor.
The insertion process involves passing the valve through the nose, down the esophagus, and into the stomach. The valve is then inflated with air or water to create a seal that prevents gastric contents from flowing back into the esophagus.
Insertion Procedure
- Measure the length of the NG tube from the tip of the nose to the stomach.
- Lubricate the tip of the NG tube with water-soluble lubricant.
- Insert the NG tube through the nose and gently advance it down the esophagus.
- When the NG tube reaches the stomach, inflate the balloon with air or water.
- Secure the NG tube in place with tape or a securing device.
Removal Procedure
- Deflate the balloon by aspirating the air or water.
- Gently pull the NG tube out through the nose.
- Dispose of the NG tube in a biohazard container.
Complications
NG tube anti-reflux valves, while beneficial, can be associated with certain complications. Understanding these potential risks and implementing preventive measures are crucial for safe and effective use.
Complications can arise due to improper insertion, malfunctioning of the valve, or prolonged use. To minimize these risks, healthcare professionals should be thoroughly trained in the correct insertion and removal techniques, and patients should be closely monitored for any signs of complications.
Prevention and Management
- Proper Insertion:Ensuring correct placement of the NG tube and anti-reflux valve is essential to prevent complications. This involves careful measurement and insertion, followed by verification using X-ray or other imaging techniques.
- Regular Monitoring:Patients should be closely monitored for any signs of complications, such as pain, discomfort, or changes in respiratory status. Regular assessments and documentation of the patient’s condition are crucial.
- Prompt Removal:If complications occur, the NG tube and anti-reflux valve should be removed promptly. This may involve deflating the balloon or using a stylet to facilitate removal.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Monitoring patients with an NG tube anti-reflux valve is crucial to ensure its proper function and prevent complications. Routine maintenance is also essential to maintain the valve’s integrity and effectiveness.
Monitoring
Monitoring should include:
- Checking the patient’s vital signs, including respiratory rate and oxygen saturation.
- Assessing the patient’s tolerance of the tube and valve, such as gagging or coughing.
- Monitoring the amount and character of gastric secretions drained through the tube.
- Observing the patient for signs of infection, such as fever, chills, or drainage from the insertion site.
Maintenance
Routine maintenance of the NG tube anti-reflux valve involves:
- Cleaning the valve with a mild soap and water solution.
- Inspecting the valve for any damage or leaks.
- Replacing the valve as directed by the manufacturer or healthcare provider.
Nursing Considerations: Ng Tube Anti Reflux Valve
Nursing considerations are crucial in managing patients with NG tube anti-reflux valves. Nurses play a vital role in monitoring, educating, and supporting these patients to ensure optimal outcomes.
Nurses should:
Monitoring
- Monitor patients closely for any signs of aspiration, such as coughing, choking, or respiratory distress.
- Observe the patient’s gastric residual volume to assess the effectiveness of the valve.
- Inspect the NG tube and valve regularly for any damage or displacement.
Education
- Educate patients on the purpose and function of the NG tube anti-reflux valve.
- Instruct patients on proper care and maintenance of the NG tube and valve, including cleaning, flushing, and changing.
- Inform patients about the signs and symptoms of potential complications.
Support
- Provide emotional support to patients and their families, as having an NG tube can be uncomfortable and stressful.
- Assist patients with nutritional management, ensuring they receive adequate nutrition while minimizing the risk of aspiration.
- Collaborate with other healthcare professionals, such as physicians, dietitians, and respiratory therapists, to provide comprehensive care.
Patient Education
Patient education is paramount for successful use of NG tube anti-reflux valves. It empowers patients with the knowledge and skills to manage their condition effectively, reducing the risk of complications and enhancing their overall well-being.
The information provided to patients should include:
Importance of the Valve
- Explaining the purpose of the valve in preventing gastric reflux and its potential benefits, such as reduced aspiration risk, improved respiratory function, and enhanced comfort.
Proper Usage
- Demonstrating how to check the valve’s function by blowing air into it.
- Instructing on how to position the patient to optimize valve function.
- Explaining the importance of maintaining the valve’s orientation to prevent reflux.
Monitoring and Maintenance
- Educating patients on signs and symptoms of valve malfunction, such as increased secretions, coughing, or respiratory distress.
- Providing instructions on how to assess valve function and troubleshoot minor issues.
- Emphasizing the importance of regular valve cleaning and replacement as per healthcare provider’s instructions.
Potential Complications, Ng tube anti reflux valve
- Discussing possible complications associated with valve use, such as esophageal perforation or valve displacement.
- Informing patients about the importance of seeking medical attention if any complications arise.
Contact Information
- Providing patients with contact information for healthcare providers or resources for further support and guidance.
Q&A
What is the purpose of an NG tube anti-reflux valve?
An NG tube anti-reflux valve is designed to prevent gastric contents from flowing back into the esophagus, reducing the risk of reflux and its associated complications.
How does an NG tube anti-reflux valve work?
The valve utilizes a one-way mechanism that allows gastric contents to pass into the small intestine but prevents their backflow into the esophagus.
What are the clinical indications for using an NG tube anti-reflux valve?
NG tube anti-reflux valves are primarily used to manage gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), hiatal hernias, and other conditions that cause reflux.