Dive into the fascinating world of covalent bonds with our comprehensive Covalent Bond Gizmo Answer Key. Prepare to unravel the intricacies of covalent bond formation, types, properties, and their remarkable applications in our daily lives. Embark on a captivating journey that will illuminate the fundamental building blocks of matter.
Covalent bonds, the cornerstone of molecular interactions, hold the key to understanding the behavior and properties of countless substances. From the simple molecules that make up our bodies to the complex materials that shape our world, covalent bonds play a pivotal role.
Introduction
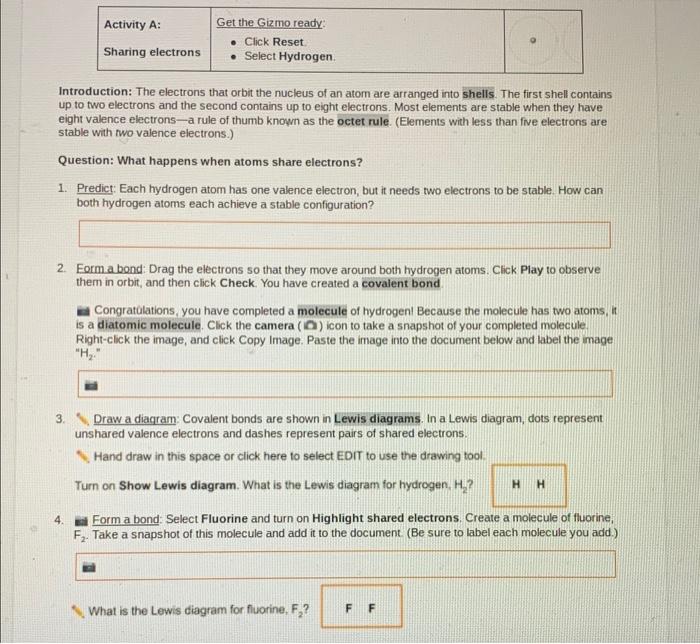
Covalent bonds are chemical bonds that involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. These bonds are formed when atoms have unpaired electrons in their outermost energy levels, also known as valence electrons. The shared electrons are attracted to the nuclei of both atoms, creating a strong bond between them.Covalent
bonds are typically found in non-metal elements and are responsible for the formation of molecules. The strength of a covalent bond depends on the number of shared electron pairs, with stronger bonds being formed when more electron pairs are shared.
Understanding the concepts behind covalent bond formation is crucial for comprehending chemical reactions. If you’re looking for a comprehensive guide to covalent bond gizmo answer key, be sure to check out the resources available online. In the realm of real estate, bert rodgers real estate book offers invaluable insights into the intricacies of the property market.
By delving into the intricacies of covalent bond formation, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of the fundamental principles governing chemical interactions.
Characteristics of Covalent Bonds, Covalent bond gizmo answer key
Covalent bonds have several characteristic features that distinguish them from other types of chemical bonds:
- Strength:Covalent bonds are generally stronger than ionic bonds but weaker than metallic bonds.
- Directionality:Covalent bonds are directional, meaning they are formed between specific orbitals on the participating atoms.
- Polarity:Covalent bonds can be polar or nonpolar, depending on the electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms.
- Saturation:Each atom can only form a limited number of covalent bonds, which is determined by the number of valence electrons it has.
Applications of Covalent Bonds: Covalent Bond Gizmo Answer Key
Covalent bonds play a vital role in numerous aspects of our daily lives and in various industries. They form the backbone of many essential materials and substances.
One prominent application of covalent bonds is in the formation of organic molecules, which are the building blocks of life. DNA, proteins, and carbohydrates all rely on covalent bonds to hold their structures together and perform their biological functions.
Importance in Industries
Covalent bonds are also crucial in the chemical industry. They enable the synthesis of a wide range of materials, including plastics, pharmaceuticals, and fuels. For example, the covalent bonds in polyethylene give it its strength and flexibility, making it suitable for use in packaging and construction.
In the semiconductor industry, covalent bonds are essential for the creation of transistors and integrated circuits. The precise arrangement of atoms and the formation of covalent bonds allow for the controlled flow of electrons, which is fundamental to the functioning of electronic devices.
FAQ Overview
What is the significance of electronegativity in covalent bond formation?
Electronegativity plays a crucial role in determining the polarity of covalent bonds. The greater the difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms, the more polar the bond becomes.
How do covalent bonds influence the properties of compounds?
Covalent bonds significantly impact the properties of compounds. Compounds with covalent bonds tend to have lower melting and boiling points, are typically non-conductors of electricity, and exhibit distinct molecular shapes.