Match the ncrna with its function. – In the intricate symphony of cellular life, non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) play a pivotal role, orchestrating gene regulation, signaling pathways, and disease pathogenesis. Their functions are as diverse as their structures, ranging from microRNAs that silence gene expression to long non-coding RNAs that modulate chromatin accessibility.
This exploration delves into the fascinating world of ncRNAs, unraveling their classification, functions, and mechanisms of action. We will illuminate the potential of ncRNAs as therapeutic targets and diagnostic biomarkers, showcasing their profound impact on human health and disease.
Define non-coding RNA (ncRNA)

Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) are RNA molecules that do not encode proteins. They are transcribed from DNA but do not undergo translation. ncRNAs are involved in a wide range of cellular processes, including gene regulation, cellular signaling, and disease pathogenesis.
Classify different types of ncRNA
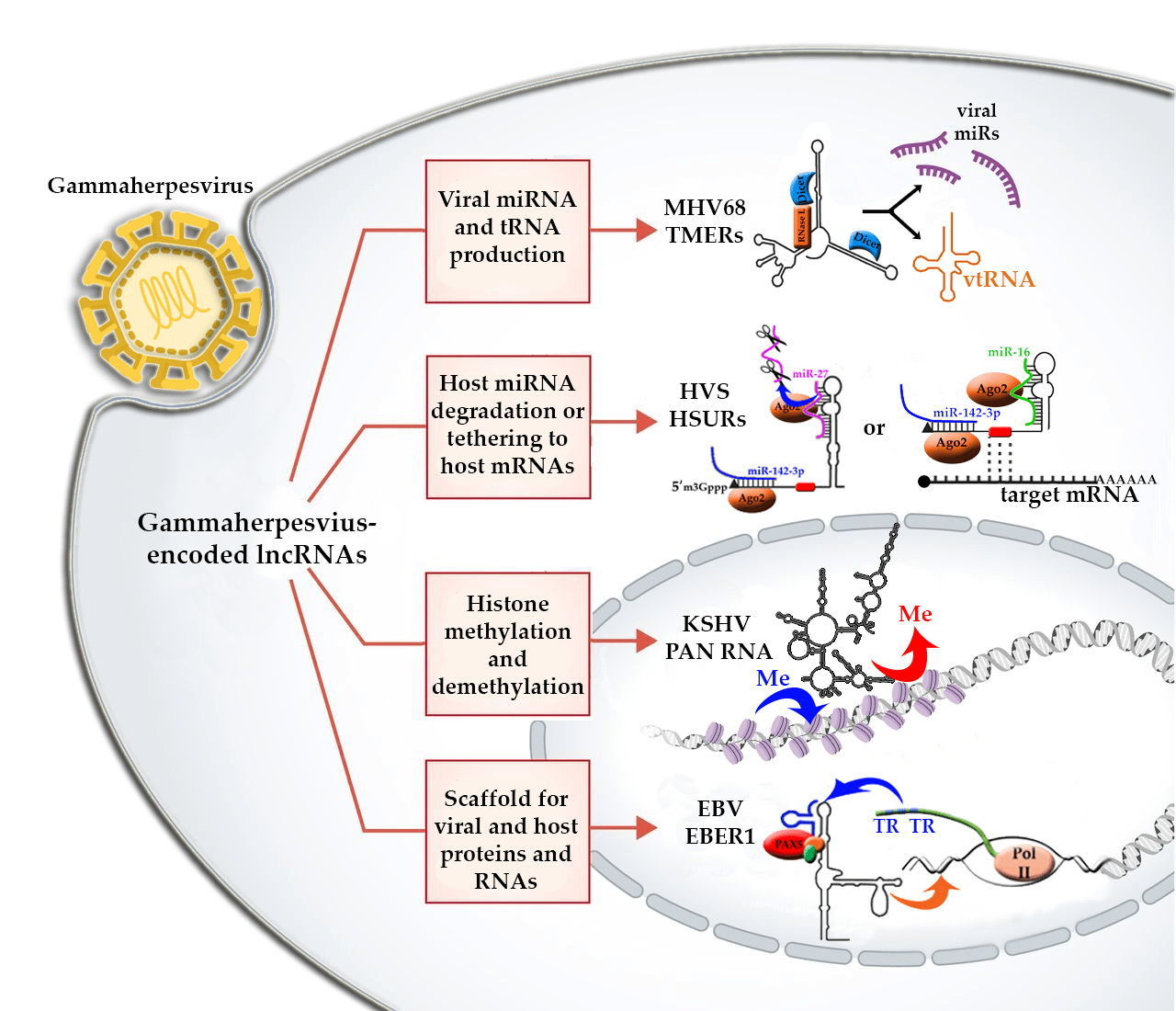
MicroRNA (miRNA)
miRNAs are small ncRNAs that are typically 20-25 nucleotides in length. They are involved in gene regulation by binding to the 3′ untranslated region (UTR) of target mRNAs and inhibiting their translation.
Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA)
lncRNAs are a class of ncRNAs that are greater than 200 nucleotides in length. They are involved in a wide range of cellular processes, including gene regulation, cellular signaling, and disease pathogenesis.
Small interfering RNA (siRNA)
siRNAs are small ncRNAs that are typically 20-25 nucleotides in length. They are involved in gene regulation by binding to the 3′ UTR of target mRNAs and triggering their degradation.
Explore the functions of ncRNA
Gene regulation, Match the ncrna with its function.
ncRNAs are involved in gene regulation by binding to target mRNAs and inhibiting their translation or triggering their degradation. This can lead to changes in gene expression and cellular phenotype.
Cellular signaling
ncRNAs can also act as signaling molecules, binding to proteins and other molecules to modulate their activity. This can lead to changes in cellular signaling pathways and cellular behavior.
Disease pathogenesis
ncRNAs have been implicated in the pathogenesis of a wide range of diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders. Dysregulation of ncRNA expression can lead to changes in gene expression and cellular signaling, which can contribute to disease development.
Illustrate the mechanisms of action of ncRNA
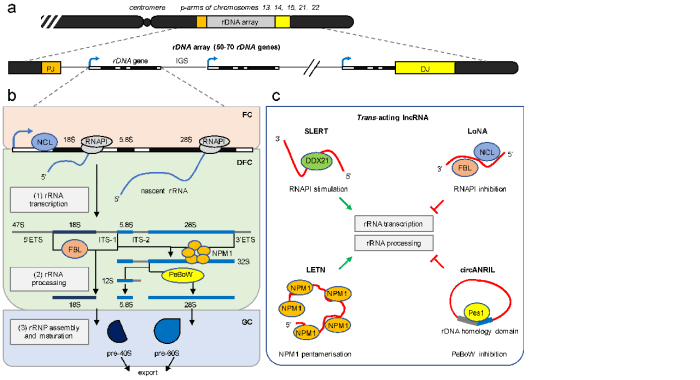
miRNA-mediated gene regulation
miRNAs bind to the 3′ UTR of target mRNAs and inhibit their translation by recruiting the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). RISC is a multi-protein complex that contains the Argonaute protein, which cleaves the target mRNA.
lncRNA-mediated gene regulation
lncRNAs can regulate gene expression by a variety of mechanisms, including binding to transcription factors, chromatin modifiers, and other regulatory proteins. This can lead to changes in the expression of target genes.
siRNA-mediated gene regulation
siRNAs bind to the 3′ UTR of target mRNAs and trigger their degradation by recruiting the RISC complex. This leads to a decrease in the expression of the target gene.
Discuss the potential applications of ncRNA research: Match The Ncrna With Its Function.
Therapeutic potential
ncRNAs have therapeutic potential for a wide range of diseases. For example, miRNAs can be used to inhibit the expression of oncogenes in cancer cells, and lncRNAs can be used to regulate the expression of genes involved in cardiovascular disease and neurodegenerative disorders.
Diagnostic biomarkers
ncRNAs can also be used as diagnostic biomarkers for a variety of diseases. For example, the expression of certain miRNAs can be used to diagnose cancer, and the expression of certain lncRNAs can be used to diagnose cardiovascular disease and neurodegenerative disorders.
FAQ Compilation
What are non-coding RNAs?
Non-coding RNAs are RNA molecules that do not encode proteins. They play diverse roles in gene regulation, cellular signaling, and disease pathogenesis.
How do ncRNAs function?
ncRNAs can function by interacting with target molecules, such as mRNA, proteins, and DNA. They can regulate gene expression by silencing mRNA, modulating chromatin accessibility, or influencing protein translation.
What is the therapeutic potential of ncRNAs?
ncRNAs hold promise as therapeutic targets for a wide range of diseases. They can be used to modulate gene expression, correct genetic defects, or inhibit disease-associated pathways.