Ecological relationships pogil answers pdf – Embark on a captivating journey into the intricate web of ecological relationships with our comprehensive POGIL answers guide. Dive into the dynamic interactions between species, uncovering the delicate balance that sustains ecosystems worldwide.
This meticulously crafted guide unveils the complexities of ecological relationships, empowering you to understand the profound impact they have on the distribution, abundance, and survival of species within diverse ecosystems.
1. Define Ecological Relationships
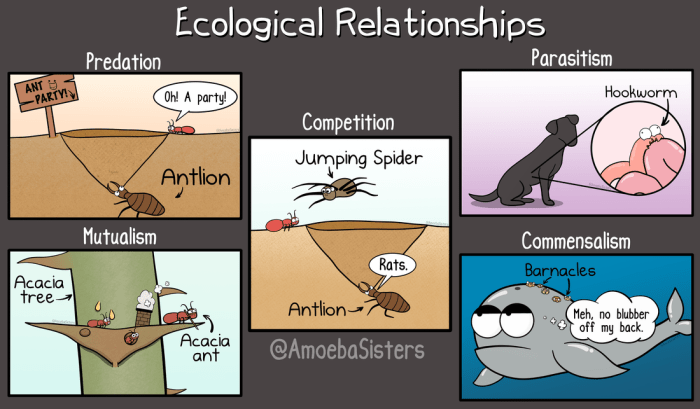
Ecological relationships are the interactions between organisms within an ecosystem. These interactions can be beneficial, harmful, or neutral, and they play a crucial role in shaping the structure and dynamics of ecosystems.
There are various types of ecological relationships, including:
- Predator-prey
- Competition
- Symbiosis
2. Types of Ecological Relationships
Mutualism
Mutualism is a symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit from the interaction. Examples include:
- Pollination by bees and flowers
- Nitrogen-fixing bacteria and legumes
Commensalism
Commensalism is a symbiotic relationship in which one species benefits while the other is neither harmed nor benefited. Examples include:
- Barnacles attached to whales
- Birds nesting in trees
Parasitism, Ecological relationships pogil answers pdf
Parasitism is a symbiotic relationship in which one species (the parasite) benefits at the expense of the other (the host). Examples include:
- Tapeworms in humans
- Mistletoe on trees
3. Competition and Predation

Competition
Competition occurs when two or more species require the same limited resources. This can lead to:
- Reduced growth and reproduction
- Territorial behavior
- Evolutionary adaptations to reduce competition
Predation
Predation is the interaction between a predator and its prey. Predators consume prey to obtain energy, while prey evolve defenses to avoid predation. Predation plays a crucial role in:
- Controlling prey populations
- Maintaining ecosystem balance
- Shaping prey behavior and morphology
4. Symbiotic Relationships: Ecological Relationships Pogil Answers Pdf

Obligate Symbiosis
Obligate symbiosis is a relationship in which both species cannot survive without each other. Examples include:
- Lichen (algae and fungi)
- Mycorrhizae (fungi and plant roots)
Facultative Symbiosis
Facultative symbiosis is a relationship in which one or both species can survive independently, but the relationship provides benefits. Examples include:
- Cleaner fish and large marine animals
- Ants and acacia trees
5. Ecological Relationships in Practice
Ecological relationships are used in various conservation and management practices, including:
- Identifying and protecting keystone species
- Controlling invasive species
- Managing wildlife populations
Understanding ecological relationships is essential for:
- Sustainable resource use
- Biodiversity conservation
- Addressing environmental challenges
FAQ
What are the key types of ecological relationships?
Ecological relationships encompass a diverse array of interactions, including predator-prey, competition, mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism.
How does competition influence species distribution?
Competition plays a crucial role in shaping species distribution by limiting access to resources, leading to niche partitioning and coexistence or exclusion.
What are the benefits and drawbacks of symbiotic relationships?
Symbiotic relationships offer both advantages and disadvantages. Mutualism provides mutual benefits, while commensalism benefits one species without harming the other. Parasitism, on the other hand, benefits one species at the expense of the other.