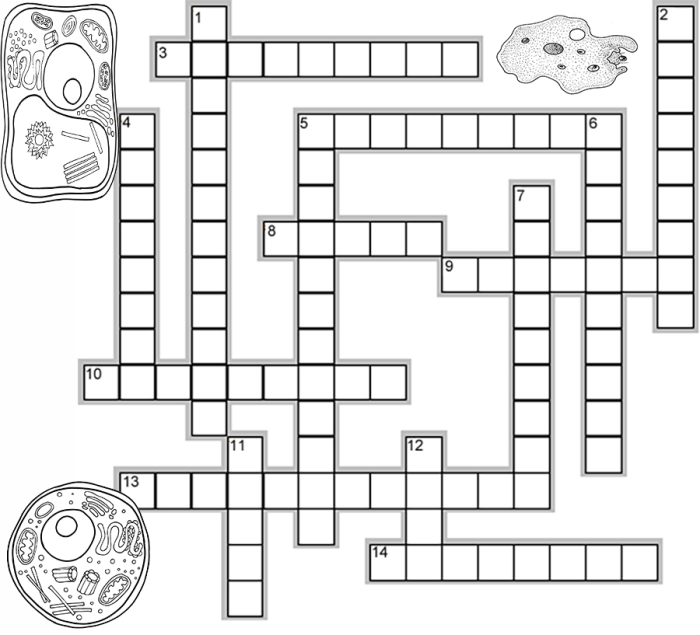
Embark on an enthralling journey into the intricate world of cells with our comprehensive guide to the Cell Structure and Function Crossword Answer Key. This captivating resource unravels the mysteries of cell biology, providing a profound understanding of the fundamental building blocks of life.
Delve into the fascinating relationship between cell structure and function, exploring how the specialized components of cells orchestrate a symphony of vital processes. Discover the diverse types of cells, each tailored to perform unique tasks that sustain the intricate tapestry of life.
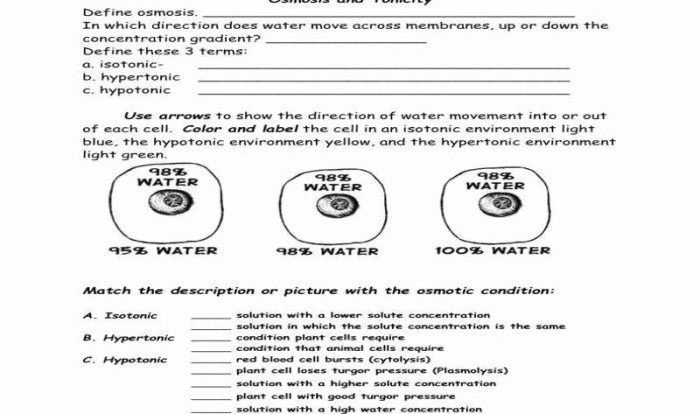
Cell Structure and Function: Cell Structure And Function Crossword Answer Key
Cells are the basic unit of life and are responsible for carrying out all of the functions necessary for life. The structure of a cell is closely related to its function, and different types of cells have specialized structures that allow them to perform specific tasks.
The basic structure of a cell includes the cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus. The cell membrane is a thin layer that surrounds the cell and regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell. The cytoplasm is the gel-like substance that fills the cell and contains the cell’s organelles.
The nucleus is the control center of the cell and contains the cell’s DNA.
There are many different types of cells, each with its own specialized structure and function. Some of the most common types of cells include:
- Epithelial cells: These cells line the surfaces of the body and protect the body from the environment.
- Muscle cells: These cells contract to produce movement.
- Nerve cells: These cells transmit electrical signals throughout the body.
- Red blood cells: These cells carry oxygen throughout the body.
- White blood cells: These cells fight infection.
The structure and function of cells is a complex and fascinating topic. By understanding the basic structure and function of cells, we can better understand how our bodies work and how to maintain our health.
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane is a thin layer of lipids that surrounds the cell. The cell membrane is selectively permeable, which means that it allows some substances to pass through it while blocking others. The cell membrane regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell, and it also helps to maintain the cell’s shape.
The cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer. Phospholipids are molecules that have a hydrophilic (water-loving) head and a hydrophobic (water-hating) tail. The hydrophilic heads of the phospholipids face outward, while the hydrophobic tails face inward. This arrangement creates a barrier that prevents water-soluble substances from passing through the cell membrane.
The cell membrane also contains proteins that help to regulate the movement of substances into and out of the cell. These proteins include channels, carriers, and pumps. Channels are pores that allow specific substances to pass through the cell membrane.
Carriers are proteins that bind to specific substances and then transport them across the cell membrane. Pumps are proteins that use energy to move substances across the cell membrane.
The cell membrane is a dynamic structure that is constantly changing. The cell membrane is constantly being remodeled, and new proteins are constantly being inserted into the membrane. The cell membrane is also constantly being repaired, and damaged proteins are constantly being replaced.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the gel-like substance that fills the cell. The cytoplasm contains the cell’s organelles, which are small structures that carry out specific functions. The cytoplasm also contains the cell’s cytosol, which is a fluid that surrounds the organelles.
The cytoplasm is responsible for supporting the cell’s activities. The cytoplasm provides a physical framework for the cell’s organelles, and it also helps to transport materials within the cell. The cytoplasm also contains enzymes that catalyze chemical reactions.
The cytoplasm is a complex and dynamic structure. The cytoplasm is constantly changing, and new organelles are constantly being formed. The cytoplasm is also constantly being remodeled, and damaged organelles are constantly being replaced.
Nucleus, Cell structure and function crossword answer key
The nucleus is the control center of the cell. The nucleus contains the cell’s DNA, which is the genetic material that determines the cell’s characteristics. The nucleus also contains the nucleolus, which is a small structure that produces ribosomes.
The nucleus is surrounded by a nuclear envelope, which is a double membrane that protects the nucleus from the rest of the cell. The nuclear envelope contains pores that allow materials to enter and exit the nucleus.
The nucleus is responsible for controlling the cell’s activities. The nucleus controls the production of proteins, and it also controls the cell’s division.
Other Organelles
In addition to the cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus, cells also contain a number of other organelles. These organelles include the mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and peroxisomes.
- Mitochondria: Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell. Mitochondria produce energy for the cell through a process called cellular respiration.
- Endoplasmic reticulum: The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes that folds and transports proteins. The endoplasmic reticulum also contains ribosomes, which are small structures that produce proteins.
- Golgi apparatus: The Golgi apparatus is a stack of membranes that modifies and packages proteins. The Golgi apparatus also produces lysosomes.
- Lysosomes: Lysosomes are small vesicles that contain digestive enzymes. Lysosomes break down waste products and cellular debris.
- Peroxisomes: Peroxisomes are small vesicles that contain enzymes that break down harmful substances.
These organelles are essential for the cell’s survival. The organelles work together to perform the cell’s functions, and they help to maintain the cell’s homeostasis.
FAQ Overview
What is the primary function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell, maintaining its internal environment and protecting it from external threats.
What is the role of the nucleus in cell activities?
The nucleus serves as the control center of the cell, housing the genetic material and directing cellular processes through the synthesis of proteins.
How do mitochondria contribute to cell metabolism?
Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, generating energy through cellular respiration to fuel various cellular activities.