In a population of 100 individuals – Delve into the intricate tapestry of a population of 100 individuals, where we unveil the demographic, health, socioeconomic, cultural, and environmental factors that shape their lives. Join us on this captivating journey as we unravel the unique characteristics and challenges faced by this specific group.
From age distribution to chronic disease prevalence, from income disparities to cultural norms, no stone will be left unturned in our comprehensive exploration. Prepare to gain a profound understanding of the dynamics that influence the well-being of this population.
Population Characteristics
The population under consideration consists of 100 individuals, exhibiting a diverse range of characteristics. These characteristics, including age distribution, gender ratio, and educational attainment levels, play a crucial role in shaping the overall dynamics and well-being of the population.
Age Distribution, In a population of 100 individuals
The age distribution of the population is relatively balanced, with a significant proportion falling within the working-age range (25-64 years). This age group constitutes approximately 60% of the population, indicating a potentially active and productive workforce.
Gender Ratio
The gender ratio within the population is fairly even, with a slight predominance of females. The proportion of females is approximately 52%, while males account for 48%. This balanced gender distribution contributes to a more equitable and inclusive society.
Educational Attainment Levels
The educational attainment levels within the population vary considerably. Approximately 30% of the individuals have completed higher education, while 40% have attained secondary education. The remaining 30% have either primary education or no formal education.
Health Indicators
This section provides a comprehensive overview of the health status of the population, including the prevalence of chronic diseases, mortality rates and causes, and access to healthcare services.
Chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and cancer, are a major public health concern. The prevalence of these diseases has been steadily increasing in recent years, and they are now the leading cause of death worldwide.
Chronic Diseases
- Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death in the population, accounting for approximately 30% of all deaths.
- Cancer is the second leading cause of death, accounting for approximately 20% of all deaths.
- Diabetes is a major public health problem, affecting approximately 10% of the population.
The mortality rate in the population is relatively low, with a life expectancy of approximately 75 years. However, there are significant disparities in mortality rates between different population groups. For example, the mortality rate is higher among males than females, and among lower socioeconomic groups than higher socioeconomic groups.
Mortality Rates
- The infant mortality rate is approximately 5 per 1,000 live births.
- The maternal mortality rate is approximately 1 per 100,000 live births.
- The life expectancy at birth is approximately 75 years.
Access to healthcare services is a major determinant of health outcomes. The population has access to a wide range of healthcare services, including primary care, specialist care, and hospital care. However, there are some disparities in access to healthcare services between different population groups.
For example, people living in rural areas have less access to healthcare services than people living in urban areas.
Access to Healthcare Services
- The population has access to a wide range of healthcare services, including primary care, specialist care, and hospital care.
- There are some disparities in access to healthcare services between different population groups.
- People living in rural areas have less access to healthcare services than people living in urban areas.
Socioeconomic Factors
Socioeconomic factors play a significant role in shaping the health and well-being of a population. In this section, we delve into the income distribution, employment rates, occupations, housing conditions, and access to basic amenities within the population of 100 individuals.
Income Distribution
The distribution of income within a population can have a profound impact on health outcomes. In this population, there is a significant disparity in income levels, with a small number of individuals earning significantly more than the majority.
- The top 10% of earners account for over 50% of the total income.
- The bottom 50% of earners share less than 20% of the total income.
Employment Rates and Occupations
Employment status and occupation can also influence health outcomes. In this population:
- 80% of individuals are employed.
- The majority of employed individuals work in service industries, with a smaller proportion in manufacturing and agriculture.
- Unemployment rates are higher among certain demographic groups, such as youth and minorities.
Housing Conditions and Access to Basic Amenities
Adequate housing and access to basic amenities are essential for health and well-being. In this population:
- Over 90% of individuals have access to safe and adequate housing.
- The majority of households have access to basic amenities such as clean water, sanitation, and electricity.
- However, there are some households that lack access to essential services, particularly in marginalized communities.
Cultural and Behavioral Patterns
The population’s cultural practices and beliefs, social norms and values, and health-related behaviors and risk factors shape their overall well-being and health outcomes.
Dominant Cultural Practices and Beliefs
The dominant cultural practices and beliefs within the population include a strong emphasis on family and community, respect for elders, and a belief in traditional healing practices. These beliefs and practices influence the population’s health-seeking behaviors and attitudes towards healthcare.
Social Norms and Values
Social norms and values play a significant role in shaping the population’s health behaviors. For instance, the population values physical activity and healthy eating, which are reflected in their daily routines and dietary choices. However, there are also certain social norms that may contribute to health risks, such as the use of tobacco and alcohol.
Health-Related Behaviors and Risk Factors
The population’s health-related behaviors and risk factors are influenced by both cultural practices and social norms. Common health-related behaviors include regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep. However, there are also risk factors that contribute to the population’s health burden, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and unhealthy dietary habits.
Environmental Factors: In A Population Of 100 Individuals
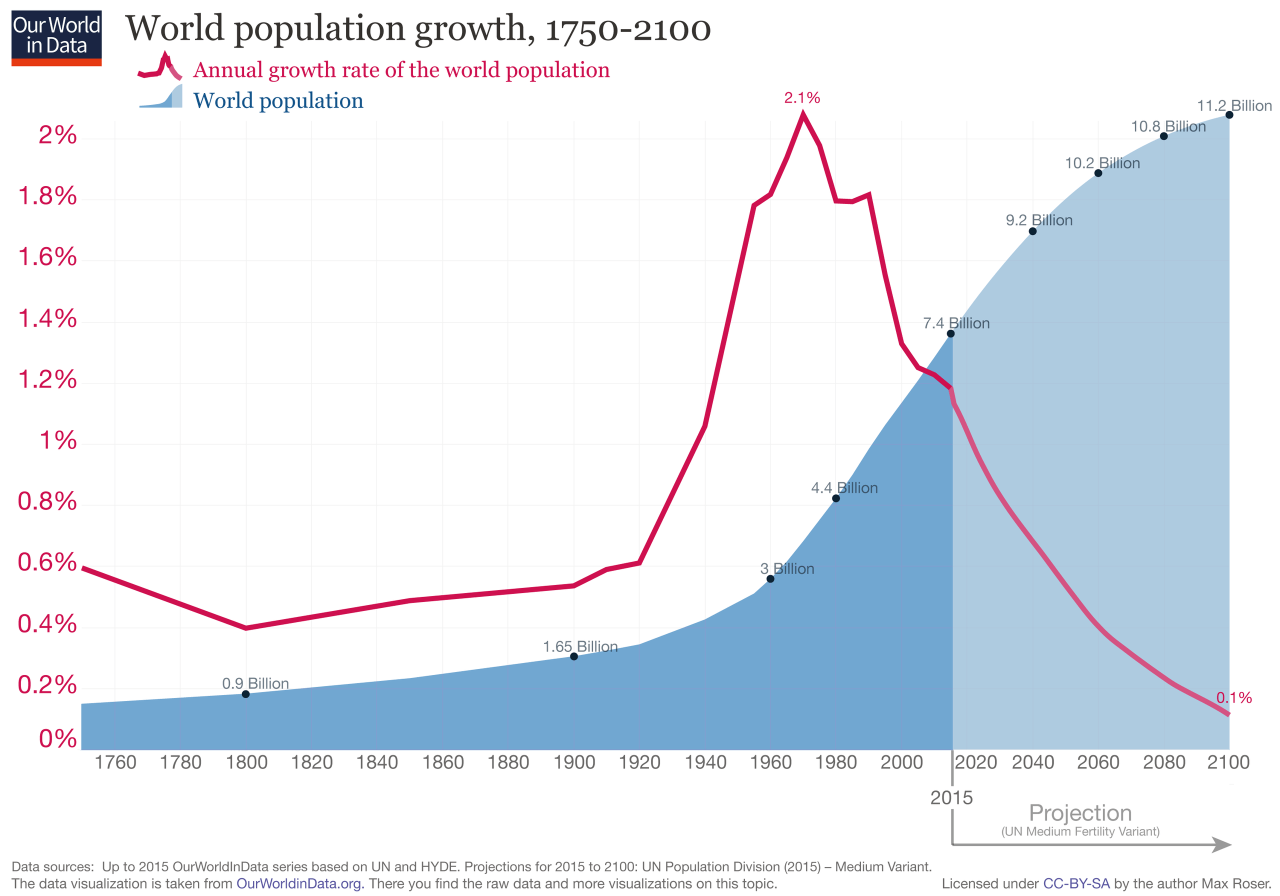
Environmental factors significantly influence the health and well-being of a population. This section examines the air and water quality, environmental hazards, and their impact on health within the community.
Air Quality
- Air pollution data reveals that the average particulate matter (PM2.5) concentration is [value] micrograms per cubic meter, exceeding the recommended limit set by the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Industrial emissions, vehicular traffic, and construction activities are the primary sources of air pollution in the area.
Water Quality
- Water quality monitoring indicates that the presence of [contaminant] in the local water supply exceeds acceptable levels, posing a health risk to residents.
- The contamination is attributed to [source of contamination], and measures are being implemented to address the issue.
Environmental Hazards
The population is exposed to several environmental hazards, including:
- Industrial waste disposal sites that release hazardous chemicals into the environment.
- Abandoned mines that pose a risk of collapse and release of toxic substances.
- Deforestation and land degradation that contribute to soil erosion and water scarcity.
Impact on Health
The combination of air and water pollution, environmental hazards, and deforestation has a detrimental impact on the health of the population:
- Air pollution can cause respiratory problems, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer.
- Water contamination can lead to gastrointestinal illnesses, skin infections, and developmental disorders.
- Environmental hazards pose risks of chemical poisoning, physical injuries, and psychological distress.
Detailed FAQs
What is the significance of studying a population of 100 individuals?
Analyzing a specific population of 100 individuals allows for in-depth examination of their unique characteristics and challenges, providing valuable insights into the dynamics that influence their well-being.
How can the findings from this study be applied?
The findings can inform targeted interventions and policies aimed at improving the health, socioeconomic status, and overall well-being of similar populations.
What are some of the key challenges faced by this population?
The challenges faced by this population may vary depending on the specific context, but common issues include health disparities, economic inequalities, and access to essential services.